Aortic Arch Abnormalities
Aortic arch abnormalities are congenital heart conditions present from birth that affect the structure and function of the aorta. Common aortic arch abnormalities detected on prenatal ultrasound include Right Aortic Arch (RAA) and Double Aortic Arch (DAA).
Right Aortic Arch
Right aortic arch (RAA) is a congenital vascular malformation where the aortic arch develops on the right side of the trachea instead of the left. Isolated RAA occurs in approximately 1 in 1000 babies and can be detected during the fetal anomaly scan.
RAA can be associated with cardiac and/ or extracardiac anomalies such as Tetralogy of Fallot and Truncus Arteriosus.
RAA has high association with chromosomal abnormalities, in particular DiGeorge syndrome which involves the deletion of a small fragment of chromosome 22q11.2 leading to a wide range of health and developmental issues.
While RAA can occur as an isolated finding, its association with chromosomal abnormalities makes genetic counselling important for affected pregnancies.
Double Aortic Arch
Double aortic arch (DAA) is a rare congenital cardiovascular malformation that occurs in approximately 1 in 10,000 pregnancies. In this condition, the foetus develops two aortic arches instead of the normal single arch, forming a vascular ring around the trachea and oesophagus.
DAA can lead to significant issues after birth due to compression of the trachea and oesophagus. Symptoms include respiratory issues (e.g. cough, wheezing, recurrent pneumonia) and gastrointestinal problems (e.g. dysphagia and choking)
DAA is also associated with other cardiovascular anomalies, including
-
Tetralogy of Fallot
-
Transposition of the great arteries
-
Atrial Septal defect
-
Ventricular Septal defect
-
Patent Ductus Arteriosus
DAA can also be associated with chromosomal abnormalities such as DiGeorge syndrome (22q11deletion).



Figure 1: Schematic diagrams of the three-vessel-trachea view in a normal fetus (A). (B) shows a right aortic arch with the transverse aortic arch to the right side of the trachea. (C) is a rare form of right aortic arch with a left ductus arteriosus (DA) forming a double aortic arch surrounding the trachea (Obgyn Key).
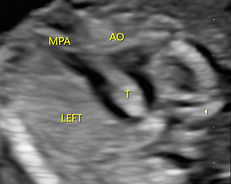

FIgure 2: Diagram on the left shows a RAA ( Obgyn Key). On the right is an 2D ultrasound image of a fetus at 18 weeks gestation with RAA.


Figure 3: Diagram on the left shows a rare form of right aortic arch with a left DA forming a DAA ( Obgyn Key). On the right is a colour-doppler of a fetus with DAA at 18 weeks gestation.
References:
Obgyn Key. “Right aortic arch and double aortic arch”. Schematic diagram. Obgyn Key. https://obgynkey.com/right-aortic-arch-double-aortic-arch-and-aberrant-subclavian-artery/ . Accessed 11 June 2025.
.jpg)